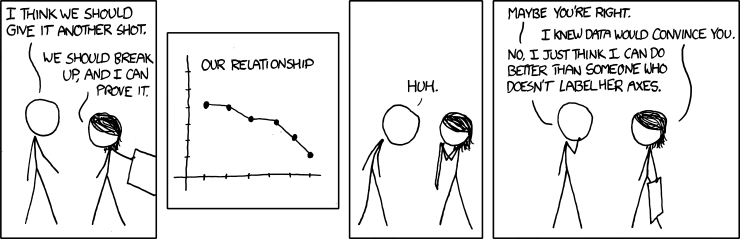
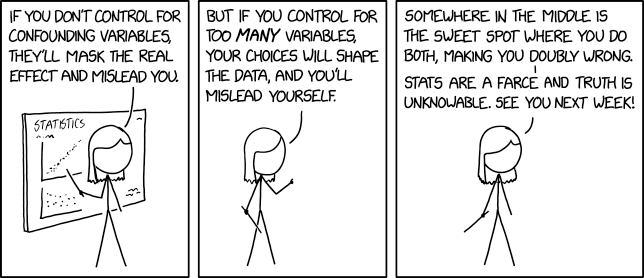
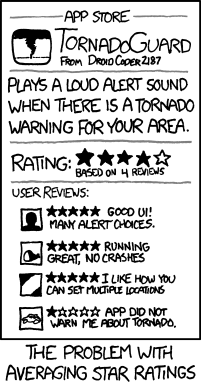
Comic of the Day
Tip: Ethical conduct is sometimes a moving target
Deadlines & Announcements
Wednesday's 8am lecture is now in CAT221
Lab 0 Mobius questions due Fri Jan 17
Chapter 1&2 assignments (Moodle) due Mon Feb 3
Watch your rounding for the assignments. Keep extra decimals for intermediate answers, then round your final answer only.
Theory Exam (Chapter 1&2) in class Mon Feb 3
Drop-in tutorials will tentatively run Tue 12-12:50 (TBC)
Today - 1.2-1.4 Sampling Methods, Experimental Design & Ethics
Notes from Moodle
Warmup
After reading the article "Is global warming still happening if it's really, really cold outside? A scientific explainer on climate change"
- what makes the author's arguments believable or not?
- what "data" (i.e. numbers) are used to support the argument, and where do those numbers come from?
- what does this have to do with a statistics class?
Try to answer these questions through the lens of Critical Evaluation:
- sampling
- bias
- analysis
Hawthorne Effect
http://www.economist.com/node/12510632
"Two groups of workers in the Hawthorne factory were used as guinea pigs. One day the lighting in the work area for one group was improved dramatically while the other group's lighting remained unchanged. The researchers were surprised to find that the productivity of the more highly illuminated workers increased much more than that of the control group.
The employees' working conditions were changed in other ways too (their working hours, rest breaks and so on), and in all cases their productivity improved when a change was made. Indeed, their productivity even improved when the lights were dimmed again. By the time everything had been returned to the way it was before the changes had begun, productivity at the factory was at its highest level. Absenteeism had plummeted.
The experimenters concluded that it was not the changes in physical conditions that were affecting the workers' productivity. Rather, it was the fact that someone was actually concerned about their workplace, and the opportunities this gave them to discuss changes before they took place."
Instead of workplace productivity, think about how you might conduct a study or experiment about workplace safety:
- what are the explanatory, response and lurking variables?
- what are the treatments?
- how could you assign treatment groups? Control group?
Next Lecture - 1.3 and 2.2 Frequency Distributions and Histograms
Pre-read 1.3 and 2.2 in the textbook and watch this 6:07 primer video on Histograms
https://www.khanacademy.org/math/pre-algebra/pre-algebra-math-reasoning/pre-algebra-picture-bar-graphs/v/histograms